Fu-yang Liu, Feng-xia Xiong, Yi-kang Fan, Juan Li, He-zhong Wang, Geng-mei Xing, Feng-ming Yan, Fu-ju Tai, Rui He
Journal of Nanoparticle Research
DOI: 10.1007/s11051-016-3642-4
【ABSTRACT】A feasible in operation, labor-saving and low-cost one-step technology to fabricate fullerenol nanoparticles (FNPs) up to 10 g in laboratory was developed by improved alkaline-oxidation approach using moderately concentrated sodium hydroxide solution as the hydroxylation agent and o-dichlorobenzene as the solvent. This strategy paves the avenue for industrial-scale bulk production of FNPs. The resulted product, [C60(OH)22·8H2O]n, were characterized by various measurements including matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, high-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, UV-Visible spectrophotometer, thermogravimetric analysis, differential scanning calorimetry, dynamic light scattering analysis, scanning electron microscopy, and electron spin resonance spectrometer. Radical scavenging assay in vitro confirmed the high efficiency of water-soluble [C60(OH)22·8H2O]n as a novel radical scavenger. Furthermore, [C60(OH)22·8H2O]n as an excellent candidate has the potential to serve as the plant defense stimulation agent in maize.
60(OH)
22·8H
2O]
n as an excellent candidate has the potential to serve as the plant defense stimulation agent in maize.
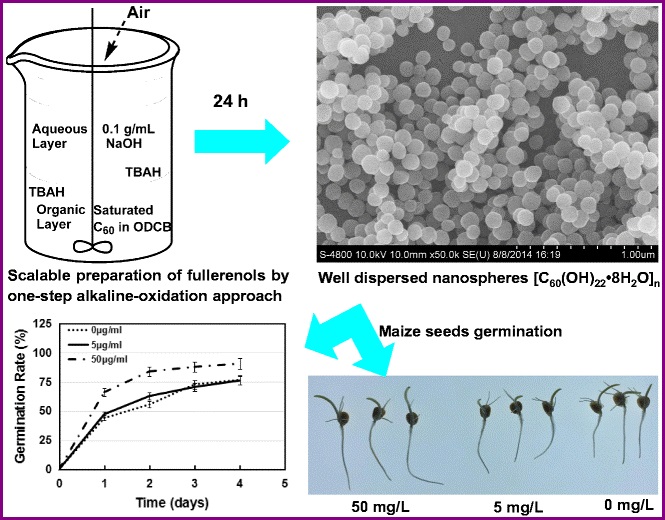 Graphical abstract
Graphical abstract


